Medical X-ray Technology
[one_half][ads1][/one_half]Without the ability to see inside the human body, doctors would find it much more difficult to diagnose and treat many different kinds of injuries and illnesses. But physicians can’t just cut into patients every time they need a better view. That’s why diagnostic imaging (such as medical x-ray technology) was invented.Yet, as familiar as most people are with x-rays, many don’t realize just how much other non-invasive (or minimally invasive) technology exists to help medical teams understand what’s happening inside patients. And many people even have deep misunderstandings about the healthcare workers who specialize in all of that radio-logic technology. (Hint: so-called “x-ray technicians” represent only a small part of the field).
What is an Medical X-ray Technician?
This might be the most important question on this page. A lot of people looking for a career in the healthcare field carry false assumptions about the term “x-ray technician” due to its widespread (but frequently incorrect) use. They believe the title signifies much more than it actually does. So, then, what is an x-ray technician?
An x-ray technician is :
- Someone who has a limited permit to perform only the most basic x-ray exams.
- Sometimes known as a limited x-ray machine operator (LXMO).
- Sometimes known as a limited medical radio-logic technologist (LMRT).
- Sometimes known as a radio-logic technician or limited radiology technician.
- NOT the same thing as a fully qualified radio-logic technologist.
- NOT the same thing as a radiologist.
- Sometimes the person who fixes the x-ray equipment rather than operates it.
X-ray technicians :
- Are typically permitted (depending on the state they work in) to carry out only the kinds of routine x-ray exams (i.e., on patient chests, arms, legs, hands, or feet) that are sometimes done in outpatient doctors’ offices.
- Often find it difficult to get work in hospitals due to their limited abilities.
- Are frequently medical assistants first and foremost who obtain limited x-ray training as part of their primary career training or as part of their continuing education.
- Have less than two years of core education in radio-logic technology.
The duties of true x-ray technicians can vary significantly since different states have different regulations and individual doctor’s offices will have their own unique needs. A lot also depends on whether x-ray techs bring additional skills to the table. (Are they primarily medical office assistants? Do they have phlebotomy training? Can they help in the medical billing and coding process?) In this respect, an x-ray tech’s day may be full of a lot of other tasks with only a few x-rays needed now and then.
In general, though, x-ray techs can have responsibilities that include:
- Consulting with doctors to receive the precise orders they must follow regarding the area of patient anatomy to be imaged.
- Preparing patients for basic x-ray exams of injured (or potentially injured) bones.
- Ensuring that the areas of patients that don’t need to be imaged are safely shielded from x-ray radiation during the procedures.
- Developing x-ray films or preparing digital images for use by the appropriate doctors for diagnosis and treatment plans.
- Performing basic maintenance on x-ray equipment.
- Maintaining detailed records.
- Performing assorted office duties like cleaning, filing, and handling phone calls.
Skills Required :
Key Skills
X-ray medical technicians must be detail-oriented and have strong communication skills.*
Technical Skills
Ability to operate complicated imaging equipment, such as X-ray imaging charge-coupled device (CCD) cameras, automatic or tabletop film processors, image intensifiers, image storage systems and X-ray bone densitometers.
Courses Offered :
X-ray technicians are also known as radio-logic technologists. They are trained in the use of radiography equipment to create images of a patient’s internal anatomy to aid doctors in diagnosis. X-ray technician courses are part of an associate’s degree program in radio-logic technology.
Introduction to Radiography Course
New x-ray technician students get an introduction to the mechanics and uses of radiography in this course. They become familiar with basic imaging techniques, medical terminology and radiation safety. The class discusses the importance of patient care and the legal and ethical responsibilities that accompany work in the medical field.
Radiation Biology and Protection Course
Safety is a primary concern in radiography, and a radiation protection course centers on ways to protect the x-ray technician and patient from any more exposure than is necessary. Students learn how radiation is produced, how it is measured and how it affects human biology. They also study federal and state standards for exposure and dosing limits.
Radio-graphic Procedures Course
Most radio-logic technology programs include several courses in radio-graphic procedures. These courses demonstrate how to position patients for radio-graphic images of various areas, such as the skull, chest, abdomen and spine. Students learn about anatomy to understand how to position the patient for the best image of a particular area. They then practice positioning in lab simulations.
Radio-graphic Imaging Course
Continuing from the overview in the introductory course, a radio-graphic imaging course provides a more detailed explanation of how radio-graphic imaging equipment operates. Students learn about the factors that influence image quality in x-rays and other radio-graphs, such as density, contrast and motion blur. The student should be able to recognize image quality and make adjustments if the quality is not acceptable. Course and lab work covers the use of traditional film media and modern digital imaging.
Pathology for Radiographers Course
This course discusses the properties and process of disease as it relates to radiology. Students learn about the diseases most commonly seen in radiology and how to identify signs of these diseases on radio-graphic images. The class also covers how diseases can require the x-ray technician to apply alternate imaging techniques.
Clinical Experience in Radiography Course
Radio-logic technology programs feature multiple clinic courses spaced out over the length of the program. Students get the opportunity to observe professional x-ray technicians at work and practice what they have learned under supervision in a real clinic or hospital. Beyond the opportunity to practice examinations, this class also gives students the chance to interact with real patients and demonstrate proper patient care.
Eligibility & Admission Process :
Colleges :
- Indian Institute of Paramedical And Community College (I.I.P.A.C.C.), Bangalore (Karnataka).
- District Hospital, Bidar (Karnataka).
- District Hospital, Gulbarga (Karnataka).
- Dr. B.R. (Bhim Rao) Ambedkar Medical College Hospital, Bangalore (Karnataka).
- Islamia Educational Society, Gulbarga (Karnataka).
- Medical College Hospital, Bellary (Karnataka).
Job Prospects & Salaries :
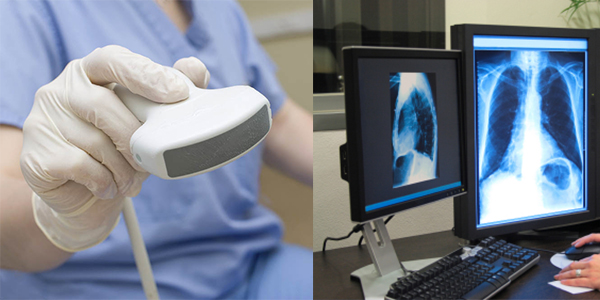
Medical x-ray technicians create x-ray images of parts of the human body using radiographic equipment, to assist in the diagnosis of medical problems. Medical x-ray technicians are often referred to as radiographers or radiologic technicians.
Medical x-ray technicians take radiographic images while performing a diagnostic imaging examination. During an x-ray procedure, a technician must position a patient’s body in a specific manner to capture the exact image ordered by the physician. Positioning may require maneuvering, turning and lifting patients with limited mobility. The technician places the imaging equipment at the correct height and angle relative to the patient’s body to produce the radiograph needed. They may take other measurements to determine the minimum effective amount of radiation needed to gather the appropriate image, and set the controls accordingly. Medical x-ray technicians need detailed knowledge of x-ray procedures and the ability to explain the procedures to a patient.
Medical x-ray techs need to be on their feet for long periods. Some medical x-ray techs work with diagnostic machines at a clinic location, while others travel to meet a patient off site. A technician may use sophisticated diagnostic equipment in vans to work outside the patient’s place of residence or even at their bedside.
Radiation Protection
Medical x-ray technicians must follow regulations for protecting patients, coworkers and themselves from unnecessary exposure to radiation from the equipment and environment. Precautions to reduce the potential hazardous radiation include gloves, aprons and other shielding devices. Badges are worn to measure the radiation in a given work area, and detailed records are kept on the accumulation of radiation exposure throughout an x-ray technician’s working life.
Specializations
Specialties for medical x-ray technicians include mammography, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and sonography. Mammographers produce images of the breast with low-dose x-rays. CT scans and MRIs image cross sections of the body to produce a 3-dimensional image. Sonographers use high-frequency ultrasound to image subcutaneous tissues, and may be used for prenatal imaging in addition to diagnosis of disorders of the abdomen, cardiovascular system, eye or brain.
Remuneration :
Medical doctors in this field can expect a salary starting from Rs.6,000 to Rs.8,000 per month for those working in government sector. For those who are working as X-ray technicians the remuneration various from Rs 5000 to Rs 8000 per month. For junior level therapists the average salary starts from Rs 4,000 to Rs 5,500 per month. On the other hand jobs in private sector are more lucrative. However, it’s significant to note that with experience and skills, a candidate can easily reach higher levels.